![]()
However, if the $5 million pertains to future dates, there is no liability amount to be reported on the current balance sheet. Hence, contingent liabilities carry much uncertainty and risk to each side of the parties involved until resolved on a future date. For contingent liabilities, the accounting treatment is different from most other types of more standard liabilities. In the case of possible contingencies, commentary is necessary on the liabilities in the footnotes section of the financial filings to disclose the risk to existing and potential investors. A conditional liability refers to a potential obligation incurred by a company on a future date if certain conditions are met.
How Does Enerpize Help Businesses In Contingent Liabilities Treatment?
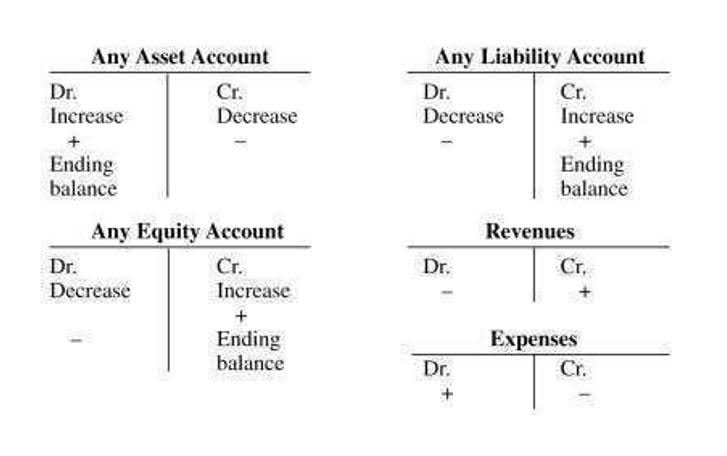
Even though they are only estimates, due to their high probability, contingent liabilities classified as probable are considered real. This is why they need to be reported via accounting procedures, and why they are regarded as “real” liabilities. In the day to day business, we can encounter some transactions whose final outcome will not be known. Some of the examples of such transactions can be insurance claims, oil spills, lawsuits. All these create a liability for the company and liabilities that are created in such situations are known as contingent liabilities. Let’s see some simple examples of the contingent liability journal entry to understand it better.
Journal Entries

Contingent liability is a potential obligation that may or may not become an actual liability in the future. In this case, the company needs to account for contingent liability by making proper journal entry if the potential future cost is probable (i.e. likely to occur) and its amount can be reasonably estimated. A contingent liability should be recorded on the company’s books if the liability is when is a contingent liability recorded probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
- At the end of the year, the accounts are adjusted for the actual warranty expense incurred.
- The chief accountant of Rey Co has reviewed the profit to date and realises they are likely to achieve profits of $13m.
- But if neither condition is met, the company is under no obligation to report or disclose the contingent liability, barring unusual circumstances.
- IFRS, under IAS 37, similarly mandates disclosures, emphasizing a narrative description of uncertainties and assumptions behind the estimates.
- This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors.
- Now imagine a lawsuit liability is possible but unlikely, with an estimated amount of $2 million.
Contingent Liabilities: Definition & Examples
Also, transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of consolidated or combined financial statements are also not required to be disclosed. The reason contingent liabilities are recorded is to adhere to the standards established by IFRS and GAAP, and for the company’s financial statements to be accurate. The matching principle of accounting states that expenses should be recorded in the same period as their related revenues. In the case of warranties, a contingent Travel Agency Accounting liability is required because it represents an amount that is not fully earned by a company at the time of sale. The expense of the potential warranties must offset the revenue in the period of sale. A contingent liability is an existing condition or set of circumstances involving uncertainty regarding possible business loss, according to guidelines from the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
- Contingent liabilities are recorded differently based on whether they are probable, reasonably possible, or remote.
- This journal entry is to show that when there is a probability of future cost which can be reasonably estimated, the company needs to recognize and record it as an expense immediately.
- If a company is being sued and it’s likely to lose the case, it must record a liability for the estimated legal settlement or penalty.
- Provisions are a sum of money that is set aside in order to cover a probable expense that will happen in future.
- The recognition of a gain contingency is not allowed, since doing so might result in the recognition of revenue before the contingent event has been settled.
Reporting Requirements of Contingent Liabilities and GAAP Compliance

If the event provides additional information about conditions that did not exist at balance sheet date, you will not recognize the subsequent event. You will only disclose a description of the event (if material) in the footnotes. Another example of a recognized subsequent event is when an allowance for doubtful accounts exists for a particular customer and then after year-end, you find out that the customer filed for bankruptcy. Even if the bankruptcy was filed after year-end, it gives more information about a circumstance that already existed at the balance sheet date (the doubt of the customer’s ability to pay).
- Another example of a recognized subsequent event is when an allowance for doubtful accounts exists for a particular customer and then after year-end, you find out that the customer filed for bankruptcy.
- This entry ensures that the financial statements reflect not only current obligations but also likely future ones, giving creditors, investors, and management a transparent view of potential risks.
- The expected cost of minor repairs would be $10,000 (10% of $100,000) and the expected costs of major repairs is $50,000 (5% of $1m).
- They believe there is a 10% chance of having to pay $12m, and a 10% chance of paying nothing.
- And, you may need to inform investors, lenders, and creditors of your contingent liabilities so they get a full picture of your company’s health.
- This disclosure does need to provide the reader details on the situation and possible loss or range of loss, or a statement that an estimate cannot be made.
Under U.S. GAAP accounting standards (FASB), the reported contingent liability amount must be “fair and reasonable” to not mislead investors or regulators. For probable contingencies, the https://wf-technology.com.ng/become-a-certified-proadvisor-quickbooks-intuit-2/ potential loss must be quantified and reflected on the financial statements for the sake of transparency. Based on the outcome of the underlying event that is set to occur in the future, the financial obligation can be “triggered” and cause the company to be held accountable to issue a conditional payment (or fee).
![]()
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Otherwise, they are disclosed in the notes or omitted entirely, depending on the likelihood and measurability. Product warranties are often cited as a contingent liability that meets both of the required conditions (probable and the amount can be estimated). Product warranties will be recorded at the time of the products’ sales by debiting Warranty Expense and crediting to Warranty Liability for the estimated amount. A loss contingency that is remote will not be recorded and it will not have to be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. An example is a nuisance lawsuit where there is no similar case that was ever successful.
